TomoWave NIR-I & NIR-II In vivo 3D Optoacoustic Imaging System
Imaging wavelength 660-1064 nm / 660-2300 nm, NIR-I & NIR-II full-band continuous imaging
X-Y-Z isotropic resolution of 3D space is 150 μm
Light absorption contrast 0.03 [1/cm] (~1pmole of ICG)
Full field imaging of mouse body and brain (40 mm x 40 mm x 40 mm)
Imaging depth > 4.5cm@mouse
Detail
Product Principles
Optoacoustic imaging is an emerging noninvasive hybrid imaging technology that combines optical excitation and ultrasonic detection. During the imaging process, the optoacoustic contrast agent absorbs a non-ionizing pulse laser and converts it into heat, which generates sound waves through thermoelastic expansion. These sound waves are detected using broadband ultrasonic transducers and optoacoustic images can be constructed according to the arrival time of the sound waves. Compared with photons, phonons scatter less in biological tissues, so optoacoustic imaging has the advantages of high tissue contrast, high spatial resolution and deep imaging. Compared with traditional near infrared region I (NIR- I,600-900 nm) optoacoustic imaging, the near infrared region II (NIR- II, 900-1700 nm) optoacoustic imaging showed higher penetration and lower tissue absorption and scattering.
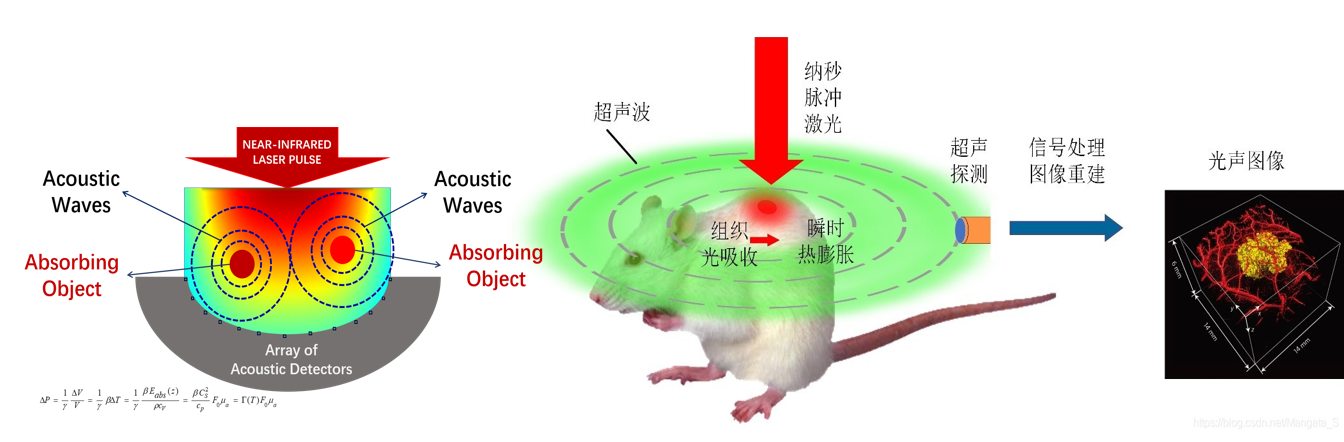
Product Characteristics
The LOIS-3D system can achieve NIR-I & NIR-II optoacoustic imaging effects because its excitation wavelength can reach 660-2300 nm. It can perform 2D and 3D imaging of the biological characteristics of living animals and obtain qualitative and quantitative data, providing more accurate diagnostic analysis for drug targeted therapy, early tumor screening, cardiovascular disease and brain disease monitoring and other research.
Imaging wavelength 660-1064 nm / 660-2300 nm, NIR-I & NIR-II full-band continuous imaging
X-Y-Z isotropic resolution of 3D space is 150 μm
Light absorption contrast 0.03 [1/cm] (~1pmole of ICG)
Full field imaging of mouse body and brain (40 mm x 40 mm x 40 mm)
Imaging depth > 4.5cm@mouse
Application Fields
Can realize 3D optoacoustic imaging of small animals in the NIR-I & NIR-II (660-2300 nm), high-resolution imaging of blood vessel morphology, and highly specific functional detection of different tissue components. Realizes multi-scale tracing and functional imaging from cells to tissue, and has important applications in many biomedical fields, such as molecular probes, bio-nanomaterials, cardiovascular diseases (angiogenesis, myocarditis, thrombosis, myocardial infarction,etc.), hemoglobin monitoring, early tumor detection and efficacy monitoring, sentinel lymph node monitoring, brain imaging and brain function monitoring and other frontier research.
Development of bio-nano materials
Development and application of photothermographic agents
Development and application of bio-nano materials
Biodistribution of nanoprobes
Blood concentration
Targeted tumor imaging
Subcutaneous tumor
In situ tumors of the brain
Orthotopic tumor of lower extremity
Prostate tumor
Anatomy imaging
Organs and spine
Cardiovascular System
Blood vessel microstructure
Brain structure and blood vessels
Synergistic treatment
Optoacoustic cavitation
Photothermal and Acoustic
Dynamics
Optoacoustic and photochemistry
Application
Labeled photoacoustic imaging - bio-nano probe in situ brain tumor imaging
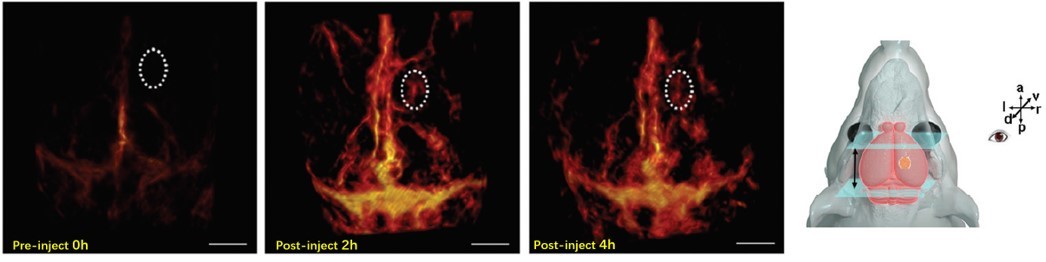
CuS nanoprobes modified with targeted peptides were used to specifically target the in situ tumor imaging under the skull at 1064nm in the NIR II region. The photoacoustic signal at the tumor site is strong, and it is an effective photoacoustic contrast agent for diagnosis.
Labeled photoacoustic imaging - bio-nano probe tumor imaging
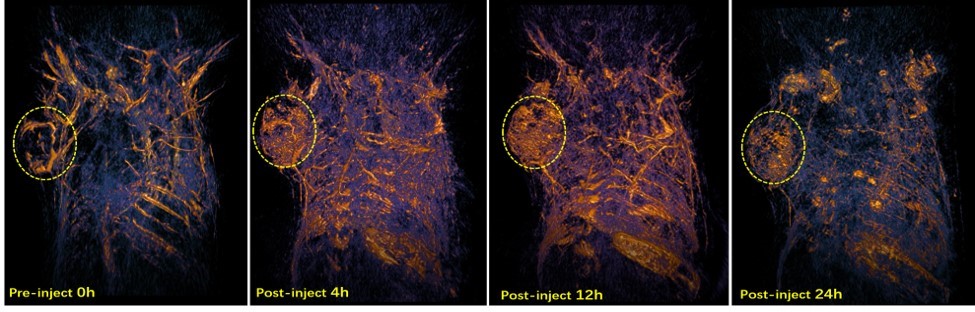
The use of organic near-infrared two-region photosensitizer targeting tumor probe 1064nm targeting subcutaneous tumor imaging can assist the preclinical diagnosis and treatment of tumor diseases.
Unlabeled photoacoustic imaging - microscopic vascular structure imaging
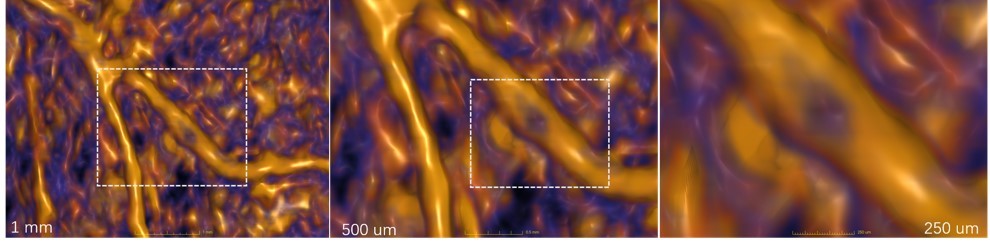
Hemoglobin microscopic angiography can observe the lesions of hematoma and possible lesions and plaques in the surrounding area of hematoma to detect cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, myocarditis, thrombosis, myocardial infarction, etc.
Unlabeled photoacoustic imaging - cerebral vascular imaging
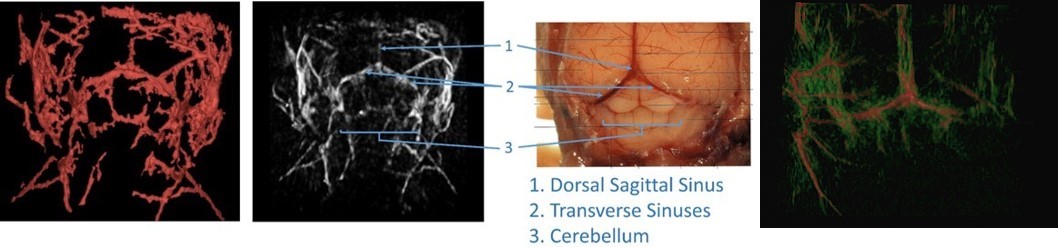
Brain vascular hemoglobin imaging can be used to detect brain tumors and traumatic brain injury (traumatic brain injury), as well as cerebrovascular leakage monitoring and efficacy evaluation, such as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cerebral stroke and so on.
Unlabeled photoacoustic imaging--Venous/arterial imaging
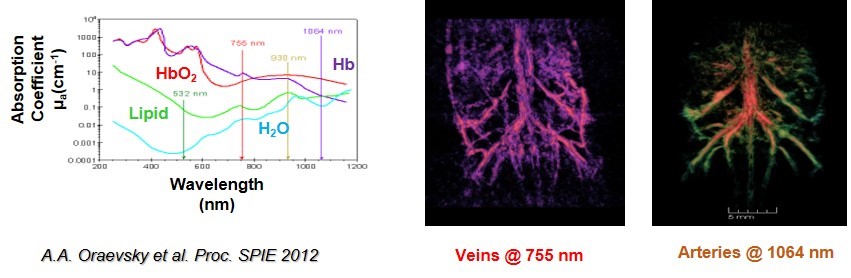
Haemoglobinography showed good anatomical features multifunctional. The figure shows the imaging of mouse organs, bones, superficial blood vessels and kidney vessels.
Unlabeled photoacoustic imaging - Organ and superficial vascular imaging
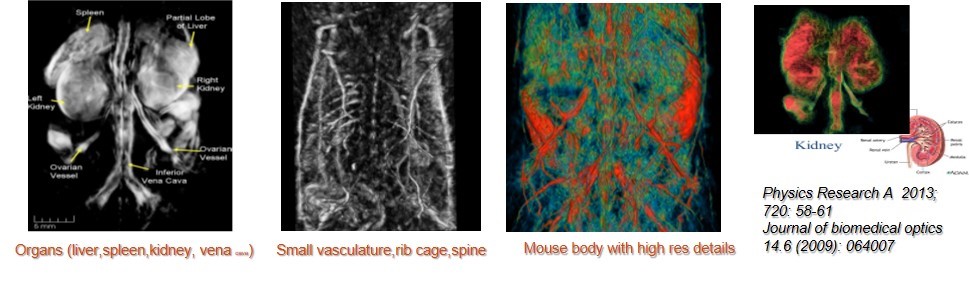
Haemoglobinography showed good anatomical features multifunctional. The figure shows the imaging of mouse organs, bones, superficial blood vessels and kidney vessels.

